The Loup Frontier Tech Index tracks the performance of publicly-traded companies that influence the future of technology including AI, robotics, autonomous vehicles, computer perception, and virtual and augmented reality. We will be publishing periodic pieces, to highlight specific companies in the index and their impact on frontier tech.
Baidu’s leadership in frontier tech and autonomous vehicles is fueled by its dominance in the Chinese search market. The company enjoys ~80% market share in search in China. Search represented 62% of Baidu’s overall revenue in 2018 (+9% y/y) generating a 38% operating margin.
“Our competitive advantage is that we have the best matching capability between users and the content. So we can distribute the content more efficiently than everyone else, be it search, newsfeed or short video feeds.” – Robin Li, Baidu CEO
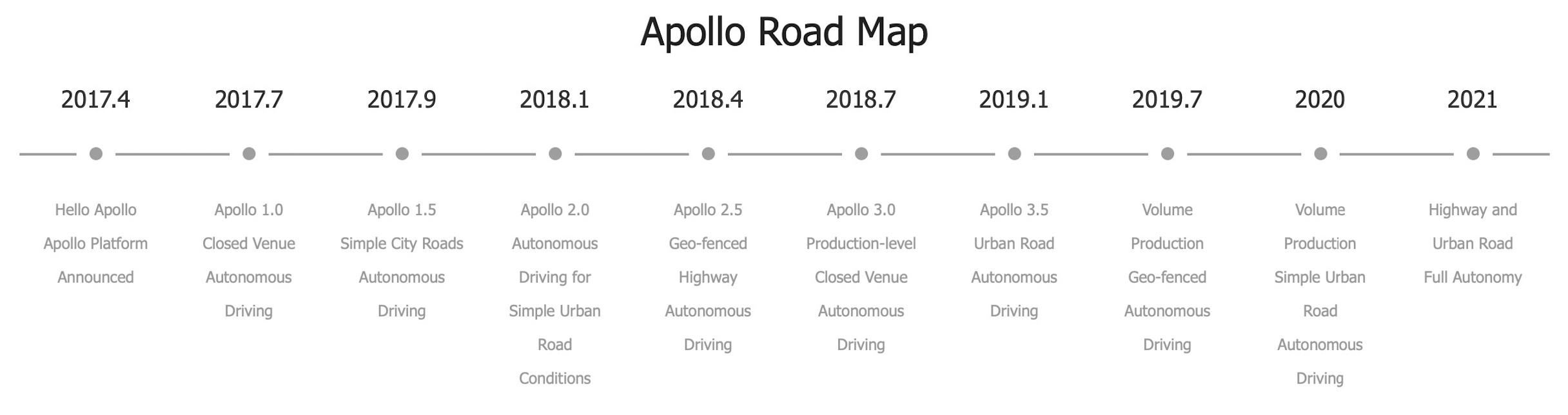
Like Google, Baidu uses its search profit engine to fund experiments in other areas like self-driving vehicle technology (Apollo). Baidu’s COO Qi Lu described Apollo as, “the Android of the autonomous driving industry.” To that end, the Apollo site lists 130 partners including Volvo, VW, Daimler, Hyundai, Ford, Jaguar Land Rover, Intel, and Nvidia. Apollo outlines their progress on the following roadmap. Apollo reached urban road autonomous driving in Jan. 2019 and expects to achieve Level 4 autonomy in 2021.
Baidu’s recently announced partnerships with Ford, FAW, and Volvo will help deliver on Apollo’s expectation to have a fleet of 100 autonomous taxis operating in China this year. Apollo provides the autonomous system’s software and automakers provide the vehicle hardware. Baidu has also built a fleet of 100 self-driving buses in China via its partnership with King Long.
Further extending the open-sourced platform’s reach, Apollo recently began offering its sensor unit for pre-order. Similarly, Waymo will begin selling its lidar system to companies that do not compete with its core autonomous ride-hailing service, as reported by Bloomberg. These efforts give the broader market access to field-tested sensor units, but also help these companies produce them at scale with more attractive costs.
Waymo ticked over 10M autonomous miles in October 2018 and has several hundred riders enrolled in its self-driving car service in suburban Phoenix. Comparatively, Apollo is widely viewed as being 3 to 4 years behind Waymo. The company began testing its software on public roads in late 2017. However, the Chinese government has both the will and the freedom to ease regulations on self-driving cars and clear the way for Apollo to advance rapidly. Baidu is well positioned to be a fast follower in autonomy.
Disclaimer: We actively write about the themes in which we invest or may invest: virtual reality, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and robotics. From time to time, we may write about companies that are in our portfolio. As managers of the portfolio, we may earn carried interest, management fees or other compensation from such portfolio. Content on this site including opinions on specific themes in technology, market estimates, and estimates and commentary regarding publicly traded or private companies is not intended for use in making any investment decisions and provided solely for informational purposes. We hold no obligation to update any of our projections and the content on this site should not be relied upon. We express no warranties about any estimates or opinions we make.
